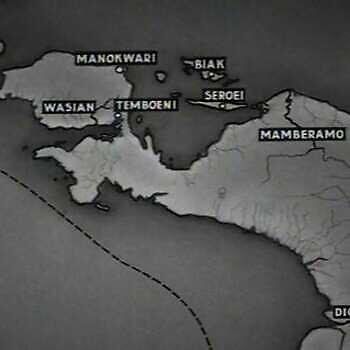
Dutch New Guinea was an overseas territory of the Netherlands from 1949 to 1962. After the transfer of sovereignty to Indonesia, the Netherlands retained this territory. The goal of the Netherlands was twofold. On the one hand, the Netherlands wanted to use New Guinea as a Dutch sphere of influence. On the other hand, it wanted to develop New Guinea and emancipate the population to prove that the Netherlands, as a colonial power, had not failed.
The Netherlands quickly responded to President Truman's declaration of the "Point Four Programme," which is seen as the beginning of modern development cooperation. This was partly because this mean the expertise in tropical agriculture, which had been acquired in the Dutch East Indies, to be put to use.
In 1962, there was a settlement of the Dutch-Indonesian dispute over New Guinea.
Extra information and sources:
- Andere tijden: het einde van Nieuw-Guinea
- IS Geschiedenis: Nederland stuurt militairen naar Nieuw Guinea
- Paul Hoebink, Hoe de dominee de koopman versloeg (Internationale Spectator 2006)
- Wikipedia- Nederlands-Nieuw-Guinea
- Jansen van Galen, John (2013), Afscheid van de koloniën; het Nederlandse dekolonisatiebeleid 1942-2010, Uitgeverij Atlas Contact, Amsterdam. Ook beschikbaar als e-book.
- Limpach, Remy (2016), De brandende kampongs van generaal Spoor, Amsterdam. Ze vielen als gemaaid koren (2022).
- Reybrouck, David van (2020), Revolusi; Indonesië en het ontstaan van de moderne wereld
NICC collection:
- A07512: Een daad van vrije keuze. De Papoea's van westelijk Nieuw-Guinea en de grenzen van het zelfbeschikkingsrecht, P.J. Drooglever (2005).
Video's:
- Beeld en Geluid: Video report from Netherlands New Guinea 1954
- Beeld en Geluid: Video Nieuw-Guinea kroniek: opleidingsmogelijkheden voor de Papoea 1957
- Beeld en Geluid: Video report from Netherlands New Guinea 1958